| Version 3 (modified by , 11 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
Source Tarballs
The source tarballs (pidgin-$VERSION.tar.gz and pidgin-$VERSION.tar.bz2) are signed with GPG by on of the following people:
| Signer | Key Signature |
| Mark Doliner | 4C292FCC
|
| Ethan Blanton | 771FC72B
|
| Stu Tomlinson | A9464AA9
|
The signatures for the source tarballs (pidgin-$VERSION.tar.gz and pidgin-$VERSION.tar.bz2) are provided as separate $FILENAME.asc downloads from the same sourceforge download directory.
You can verify a tarball by downloading both the tarball and its corresponding .asc file:
gpg --verify $FILENAME.asc
If you haven't already imported the key that was used to sign the tarballs, you'll get a message about an unknown key when you attempt to verify; you'll need to import one of the above key signatures from a public keyserver (e.g. pgp.mit.edu):
gpg --keyserver pgp.mit.edu --recv-key $KEYSIGNATURE
You can read more about how the signing and verification works in the GPG Handbook.
Windows Installers
As of Pidgin 2.10.7, the Windows installers are signed using the Microsoft Authenticode signing mechanism by Daniel Atallah using a key with a thumbprint of C5476901C3C63FABF54CEBA9E3F887932A9579B5.
The signature can be verified most easily by using Windows Explorer to look at the Properties of the installer executable.
In the "Digital Signatures" tab, you can look at the Details of the signature, "View Certificate", and compare the (case-insensitive, whitespace-insensitive) "Thumbprint" value in the "Details" tab to the value listed above.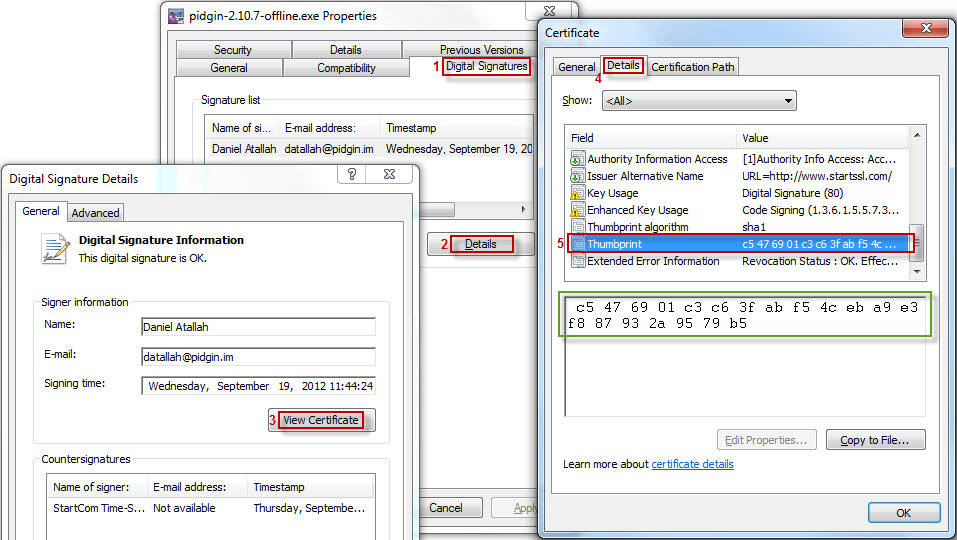
Alternatively, the signature can be verified using Microsoft's signtool.exe utility (which, unfortunately, in order to obtain, requires that you install the at least parts of Microsoft Platform SDK).
Attachments (1)
-
windows_cert_verify_thumbprint.jpg (97.6 KB) - added by 11 years ago.
Image showing the steps to verify the window signing certificate's thumbprint.
Download all attachments as: .zip

